|
January 1964 Popular Electronics
 Table of Contents Table of Contents
Wax nostalgic about and learn from the history of early electronics. See articles
from
Popular Electronics,
published October 1954 - April 1985. All copyrights are hereby acknowledged.
|
Of all the ones to miss
on this "Three Letter Quiz," I screwed up drawing "A." It was a matter of thinking
too hard (at least that's my excuse). This is another of Robert P. Balin's
many electronics-related quizzes that appeared in Popular Electronics magazine
over a couple of decades. I will once again admonish non-old guys (unlike myself)
to not spaz when you see a vacuum tube in the circuit. Just mentally replace it
with an equivalent semiconductor device (a diode if it has two elements - other
than a heater coil - or a transistor if it has three or more elements). Surely,
you will easily figure our "A," and probably the other nine as well. I colorized
the drawings to make them look more modern.
Three Letter Quiz
Quizzes from vintage electronics magazines such as Popular
Electronics, Electronics-World, QST, Radio-Electronics,
and Radio News were published over the years - some really simple and others
not so simple. Robert P. Balin created most of the quizzes for Popular
Electronics. This is a listing of all I have posted thus far.
- Oscillator
Quiz, November 1962 Popular Electronics
- Vacuum Tube Quiz,
February 1961 Popular Electronics
- Kool-Keeping Kwiz, June
1970 Popular Electronics
- Find the Brightest
Bulb Quiz, April 1960 Popular Electronics
-
Where Do the Scientists Belong? - Feb 19, 1949 Saturday Evening Post
- Quiz
on AC Circuit Theory, December 1970 Popular Electronics
- Magnetic
Phenomena Quiz, February 1962 Popular Electronics
- Electronics
Geography Quiz, April 1970 Popular Electronics
- Electronic
Menu Quiz, August 1963 Popular Electronics
- Electronic
Noise Quiz, August 1962 Popular Electronics
- Electronic
Current Quiz, October 1963 Popular Electronics
- Electronic
Inventors Quiz, November 1963 Popular Electronics
- Resistor Function
Quiz, January 1962 Popular Electronics
- Electronic
Measurement Quiz, January 1963 Popular Electronics
- Electronic
Coupling Quiz, August 1973 Popular Electronics
- Electronics
Analogy Quiz, August 1960 Popular Electronics
- Audio Quiz, April
1955 Popular Electronics
- Electronic Unit
Quiz, May 1962 Popular Electronics
- Capacitor
Circuit Quiz, June 1968 Popular Electronics
- Meter-Reading
Quiz, June 1966 Popular Electronics
- Electronic
Geometry Quiz, Jan 1965 Popular Electronics
- Electronic
Factor Quiz, November 1966 Popular Electronics
- Electronics
Math Quiz, November 1965 Popular Electronics
- Series Circuit
Quiz, May 1966 Popular Electronics
- Electrochemistry
Quiz, Mar 1966 Popular Electronics
- Biz
Quiz: Test Your Sales Ability - April 1947 Radio News
- Electronic
Analogy Quiz, Nov 1961 Popular Electronics
- Diode Quiz, July
1961 Popular Electronics
- Electronic
Curves Quiz, Feb 1963 Popular Electronics
- Electronic
Numbers Quiz, Dec 1962 Popular Electronics
- Energy Conversion
Quiz, April 1963 Popular Electronics
- Coil Function
Quiz, June 1962 Popular Electronics
-
Co-Inventors Quiz - January 1965 Electronics World
-
"-Tron" Teasers Quiz - Oct 1963 Electronics World
- Polarity Quiz
- March 1968 Popular Electronics
-
Television
I.Q. Quiz - Oct 1948 Radio & Television News
- Amplifier Quiz
Part I - Feb 1964 Popular Electronics
- Semiconductor
Quiz - Feb 1967 Popular Electronics
- Unknown
Frequency Quiz - September 1965 Popular Electronics
- Electronics
Metals Quiz - Oct 1964 Popular Electronics
- Electronics
Measurement Quiz - August 1967 Popular Electronics
- Vector-Circuit
Matching Quiz, June 1970 Popular Electronics
- Inductance
Quiz, September 1961 Popular Electronics
- RC Circuit Quiz,
June 1963 Popular Electronics
|
-
LCR Circuits Quiz - November 1969 Electronics World
- Amplifier Quiz
Part 2 - March 1964 Popular Electronics
- Amplifier
Quiz Part 1 - February 1964 Popular Electronics
- Three
Letter Quiz - January 1964 Popular Electronics
-
Electromagnetic Function - June 1964 Popular Electronics
-
Electronic Sticklers - February 1959 Popular Electronics
-
Bio-Electronic Quiz - July 1964 Popular Electronics
- Transformer Quiz
- April 1962 Popular Electronics
- Oscilloscope
Quiz - October 1961 Popular Electronics
- Roundword Puzzle
- January 1961 Popular Electronics
- Electronic
Sticklers - April 1959 Popular Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - August 1966 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - February 1966 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - September 1962 Radio-Electronics
- Electronic Sticklers
- May 1959 Popular Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - February 1963 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - April 1964 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - October 1966 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - June 1963 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - July 1966 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - December 1966 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - October 1964 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - July 1963 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - March 1966 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - November 1966 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - October 1966 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - May 1966 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - January 1966 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ - July 1966 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - December 1966 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - October 1964 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - June 1963 Radio-Electronics
-
R-E Puzzler - June 1967 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - January 1963 Radio-Electronics
-
Do You Know the Law? - Nov 1963 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - November 1962 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - September 1966 Radio-Electronics
- Radio
WittiQuiz - October 1938 Radio-Craft
-
What's Your EQ? - November 1964 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - February 1964 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - July 1967 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - December 1962 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - April 1966 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - October 1963 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - July 1964 Radio-Electronics
- Radio
WittiQuiz - November 1937 Radio-Craft
-
What's Your EQ? - May 1967 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - July 1962 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - January 1962 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - February 1962 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - March 1962 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - July 1961 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - August 1961 Radio-Electronics
-
Can You Name These Strange Electronic Effects? - August 1962 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - September 1961 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - September 1962 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - October 1961 Radio-Electronics
- Radio
WittiQuiz - December 1937 Radio-Craft
-
What's Your EQ? - November 1961 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - March 1964 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - April 1962 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - May 1962 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - June 1962 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - April 1967 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - March 1967 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - December 1964 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - January 1967 Radio-Electronics
-
Wanted: 50,000 Engineers - Jan 1953 Popular Mechanics
-
What's Your EQ? - August 1964 Radio-Electronics
- Voltage Quiz
- December 1961 Popular Electronics
-
What is It? - June 1941 Popular Science
- What Do You Know
About Resistors? - April 1974 Popular Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - September 1963 Radio-Electronics
- Potentiometer Quiz - Sep
1962 Popular Electronics
-
Mathematical Bafflers - March 1965 Mechanix Illustrated
- Op Amp Quiz -
October 1968 Popular Electronics
- Electronic "A"
Quiz - April 1968 Popular Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - May 1961 Radio-Electronics
-
Popular Science Question Bee - Feb 1939 Popular Science
-
What is It? - A Question Bee in Photographs - June 1941 Popular Science
-
What's Your EQ? - June 1961 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - June 1964 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - May 1964 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - August 1963 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - May 1963 Radio-Electronics
- Bridge
Function Quiz - Sep 1969 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - March 1963 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - February 1967 Radio-Electronics
-
Circuit Quiz - June 1966 Radio-Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - June 1966 Radio-Electronics
- Electronics
Mathematics Quiz - June 1969 Popular Electronics
- Brightest
Light Quiz - April 1964 Popular Electronics
-
What's Your EQ? - April 1963 Radio-Electronics
- Electronics "B" Quiz
- July 1969 Popular Electronics
- Ohm's Law Quiz
- March 1969 Popular Electronics
-
Antenna Quiz - November 1962 Electronics World
- Color Code Quiz
- November 1967 Popular Electronics
- CapaciQuiz
- August 1961 Popular Electronics
- Transformer
Winding Quiz - Dec 1964 Popular Electronics
-
Audiophile Quiz - November 1957 Radio-electronics
- Capacitor
Function Quiz - Mar 1962 Popular Electronics
- Greek Alphabet
Quiz - December 1963 Popular Electronics
- Circuit
Designer's Name Quiz - July 1968 Popular Electronics
-
Sawtooth Sticklers Quiz - Nov 1960 Radio-Electronics
-
Elementary
Radio Quiz - December 1947 Radio-Craft
- Hi-Fi
Quiz - October 1955 Radio & Television News
- Electronics Physics
Quiz - March 1974 Popular Electronics
- A Baffling Quiz
- January 1968 Popular Electronics
- Electronics IQ
Quiz - May 1967 Popular Electronics
- Plug and Jack
Quiz - Dec 1967 Popular Electronics
- Electronic
Switching Quiz - Oct 1967 Popular Electronics
- Electronic
Angle Quiz - Sep 1967 Popular Electronics
- International
Electronics Quiz - July 1967 Popular Electronics
- FM Radio
Quiz - April 1950 Radio & Television News
- Bridge Circuit
Quiz -Dec 1966 Popular Electronics
- Diode Function
Quiz - August 1965 Popular Electronics
- Diagram Quiz,
August 1966 Popular Electronics
- Quist Quiz - November
1953 QST
- TV Trouble Quiz,
July 1966 Popular Electronics
- Electronics History Quiz,
Dec 1965 Popular Electronics
- Scope-Trace Quiz,
March 1965 Popular Electronics
-
Electronic
Circuit Analogy Quiz, April 1973
-
Test Your Knowledge of Semiconductors, August 1972 Popular Electronics
- Ganged Switching
Quiz, April 1972 Popular Electronics
- Lamp Brightness
Quiz, Jan 1969 Popular Electronics
- Lissajous
Pattern Quiz, Sep 1963 Popular Electronics
- Electronic
Quizoo, October 1962 Popular Electronics
- Electronic
Photo Album Quiz, March 1963 Popular Electronics
- Electronic
Alphabet Quiz, May 1963 Popular Electronics
- Quiz: Resistive?
Inductive? or Capacitive?, October 1960 Popular Electronics
|
Three Letter Quiz Answers
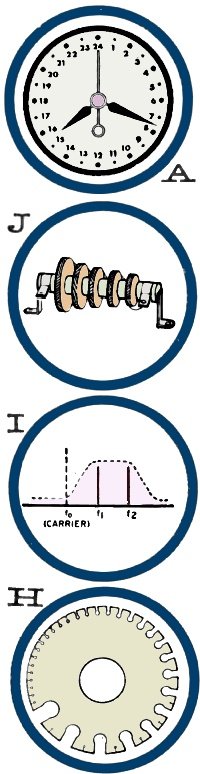
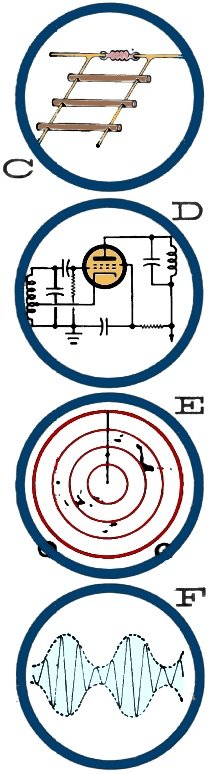
1 - H The American Wire Gauge (AWG) system is used to measure wire
diameter in the United States.
2 - D In Electron Coupled Oscillator (ECO) circuit, the screen is
the oscillator anode. Output is coupled to plate via electron stream only.
3 - A Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is time at Greenwich, Eng., meridian,
given in 24 -hour system.
4 - F Modulated Continuous Wave (MCW) is a type of tone-modulated
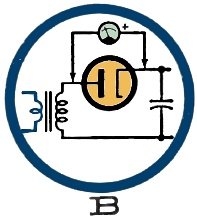
carrier wave transmitted by some commercial radiotelegraph stations.
5 - B Peak Inverse Voltage (PIV) is maximum voltage across a rectifier
in the reverse polarity.
6 - E A PPI is a radar display, Plan Position Indicator type, showing
scanned area as a map.
7 - J A radio-frequency choke (RFC) is a coil having relatively high
inductive impedance within its usable frequency range, without self-resonance.
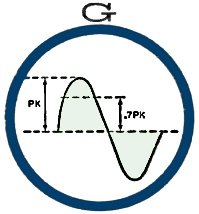
8 - G The root-mean-square (RMS) value of a sine-wave a.c. is the
value that will cause the same heating effect in a resistive load as a numerically
equal value of d.c.
9 - I In single-sideband (SSB) transmission, the carrier and one
sideband are suppressed, and only the remaining sideband is radiated.
10 - C The standing wave ratio (SWR) on a transmission line is maximum
value of current or voltage to minimum value, as measured along line.
|