|
Power is commonly expressed in decibel values in order
to make adjustments due to loses and gains. The logarithmic nature of decibel units
translates the multiplication and division associated with gains and losses into
addition and subtraction. Once you get used to it, you will never want to return
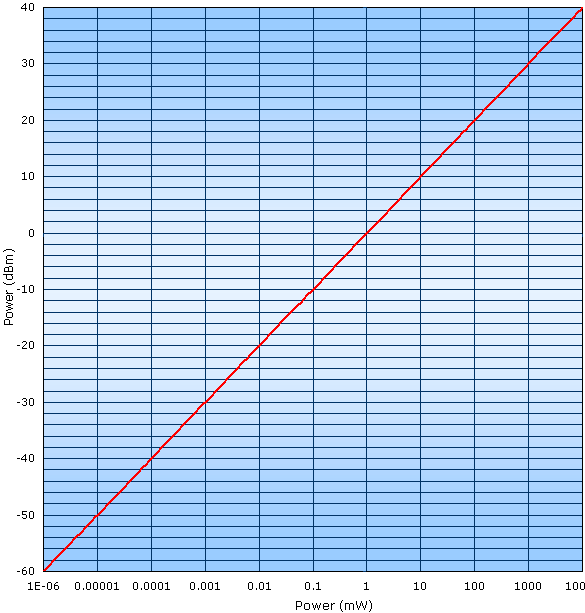
to watts. Units of dBm are decibels relative to 1 mW of power, hence, 0 dBm 1 mW.
1/100 mW is -20 dBm and 100 mW is +20 dBm. Powers less than 1 mW are always negative
dBm values, and powers greater than 1 mW are always positive. See the graph below.
Here are the formulas:
P(mW) = 10[P(dBm)/10]
P(dBm)=10*log[P(mW)]
|








