Website visitor Neil S. provided the following explanations regarding connector
name origins:
C - Concelman (Carl Conselman worked
for Ampheol)
N - Neill (Paul Neill worked for Bell Labs)
TNC - Threaded Neill-Concelman
BNC - Bayonet Neill-Concelman
An RF connector is an electrical connector designed to work at radio frequencies
in the multi-megahertz range. RF connectors are typically used with coaxial cables
and are designed to maintain the shielding that the coaxial design offers. Better
models also minimize the change in transmission line impedance at the connection.
Mechanically they provide a fastening mechanism (thread, bayonet, braces, push pull)
and springs for a low ohmic electric contact while sparing the gold surface thus
allowing above 1000 reconnects and reducing the insertion force. Research activity
in the area of radio-frequency (RF) circuit design has surged in the last decade
in direct response to the enormous market demand for inexpensive, high data rate
wireless transceivers. - Wikipedia
Here is an interesting read on
RF Connector Guide & History
Click here to see connector
usage chart.
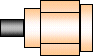
| 2.4 mm Maximum Frequency: 50 GHz
This family is not directly mateable with the SMA family. Quality grades; general
purpose, instrument, and metrology.
|
 |
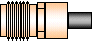 |
| 7/16 DIN Maximum Frequency: 7.5 GHz
Cellular and other "wireless" applications, especially on towers. Rated to 7.5
GHz. Low PIMs.
|
|
|
| APC-2.4 (Amphenol Precision Connector, 2.4 mm)
|
|
|
| APC-3.5 (Amphenol Precision Connector, 3.5 mm)
|
|
|
| APC-7 (Amphenol Precision Connector, 7 mm)
Maximum Frequency: 18 GHz
Offers the lowest reflection coefficient and most repeatable measurement of all
18 GHz connectors. Hermaphrodite design. Preferred connector for metrology and calibration.
|
|
|
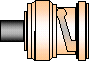
| BNC (Bayonet Navy Connector)
(Amphenol claims it's for Bayonet Neill Concelman)
Maximum Frequency: 2 GHz
OSBDesigned for military use. Wide acceptance in video and RF applications to
2 GHz.
|
 |
 |
| C Maximum Frequency: 12 GHz
Medium-size, 50 Ω impedance. Type N connectors, but are bayonet locking.
|
|
|
| F Maximum Frequency: 1 GHz
Utilized in television cable and antenna applications. 75 Ω characteristic impedance.
3/8-32 coupling thread.
|
|
|
| GR874 Maximum Frequency: 8.5 GHz
Hermaphroditic, 50 Ω impedance with a slide-on interface.
|
|
|
| GR900BT Maximum Frequency: 8.5 GHz
Hermaphrodite connectors. Used in highly critical laboratory applications at
frequencies up to
8.5 GHz.
|
|
|
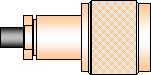
| N (Navy)
OSN
Maximum Frequency: 12 GHz
Uses an internal gasket to seal out the environment.
|
 |
 |
| RCA Maximum Frequency: 10 MHz
Round, press-on connector used for consumer-grade audio and composite video connections.
Color coded as follows: red (audio-Right), black or white (audio-Left) and yellow
(composite video).
|
|
|
| SMA (Sub-Miniature A)
OSM/3mm
Maximum Frequency: 12 GHz
One of the most commonly used RF/microwave connectors. Standard SMA connectors
are designed for interconnects to 12.4 GHz. A good SMA is useable to 18 GHz.
|
 |
 |
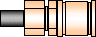
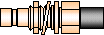
| SMB (Sub-Miniature B)
OSMB
|
 |
 |
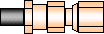
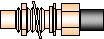
| SMC (Sub-Miniature C)
OSMC
|
 |
 |
| SSMA (Sub-SMA)
OSSM
|
|
|
| TNC (Threaded Navy Connector)
Maximum Frequency: 2 GHz
OSTThreaded version of the BNC connector. Both 50 Ω and 75 Ω versions are available.
|
 |
 |
| UHF Maximum Frequency: 300 MHz
Non-constant (characteristic) impedance, suitable for use up to 300 MHz but can
be rated for up to 500 MHz.
|
 |
 |
Related Pages on RF Cafe - Coaxial Cable
Specifications - Capacitor Dielectrics & Descriptions
- Dielectric Constant, Strength, &
Loss Tangent - Conductor Bulk Resistivity & Skin
Depths - Coaxial Cable Equations -
Coaxial Cable Specifications -
Coaxial Cable Vendors - Coaxial Resonator -
Coaxial Connector Usage Chart
|















