February 1958 Radio-Electronics
 [Table
of Contents] [Table
of Contents]
Wax nostalgic about and learn from the history of early electronics.
See articles from Radio-Electronics,
published 1930-1988. All copyrights hereby acknowledged.
|
 The world's first electric
wristwatch went on sale on
January 3,
1957 - the Ventura
model, by Hamilton Electric, and it retailed for $200. I use the event as the theme
of the RF Cafe logo for that day in history. Unlike today's electric watches which
use a crystal for timing, the early watches used a pulsed motor to energize the
balance wheel coil, in place of a mainspring and an escapement mechanism. Some
"atomic" wristwatches today like the
Casio Waveceptor (<$40) use the
WWV signals from Boulder, Colorado, to synchronize
the time with world standards. The watch
shown in this article from the
February 1958 edition of Radio-Electronics magazine is a model 500, which you can find more
detail about on the
Unique Watch Guide
website. The world's first electric
wristwatch went on sale on
January 3,
1957 - the Ventura
model, by Hamilton Electric, and it retailed for $200. I use the event as the theme
of the RF Cafe logo for that day in history. Unlike today's electric watches which
use a crystal for timing, the early watches used a pulsed motor to energize the
balance wheel coil, in place of a mainspring and an escapement mechanism. Some
"atomic" wristwatches today like the
Casio Waveceptor (<$40) use the
WWV signals from Boulder, Colorado, to synchronize
the time with world standards. The watch
shown in this article from the
February 1958 edition of Radio-Electronics magazine is a model 500, which you can find more
detail about on the
Unique Watch Guide
website.
Electric Wristwatch
 The electronic technician may soon be seeing
a new item on his workbench, the electric wrist watch. He may need a powerful magnifying
glass or two and a couple of jewelers' tools, but an electric watch is driven by
a tiny electric motor using batteries of a highly specialized type and requires
service know-how more closely allied to that of a radio technician than the jeweler. The electronic technician may soon be seeing
a new item on his workbench, the electric wrist watch. He may need a powerful magnifying
glass or two and a couple of jewelers' tools, but an electric watch is driven by
a tiny electric motor using batteries of a highly specialized type and requires
service know-how more closely allied to that of a radio technician than the jeweler.
The Hamilton Watch Co., after 10 years of research and testing, has placed an
electric wristwatch on the market. Driven by a miniature reaction motor, it has
an accuracy of 99.995% and is powered by a button battery with a life of more than
12 months.
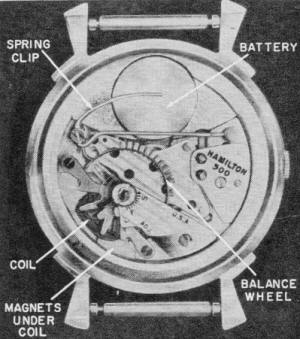
A miniature triangular coil is attached to the balance wheel which is used as
the motor's rotor. Platinum-alloy permanent magnets, claimed to have the highest
energy content of any magnet in the world today, create the motor's magnetic field.
Coil contact is made through a silver-gold-alloy contact on a nonmagnetic spring
fastened to a mounting plate (see figure). As the wheel oscillates its contact brushes
against the spring contact, sending a pulse of current through the coil. Timing
is based on the natural oscillation period of the balance wheel.

Electric Wristwatch Mechanism
Posted June 17, 2020
(updated from original post on 1/15/2014)
|











