|
August 1959 Popular Electronics
 Table
of Contents Table
of Contents
Wax nostalgic about and learn from the history of early electronics. See articles
from
Popular Electronics,
published October 1954 - April 1985. All copyrights are hereby acknowledged.
|
Author Saunder Harris wrote
in this 1959 of edition Popular Electronics magazine that the concept of
atoms has been around for more than 2,500 years since Greek philosopher Democritus
suggested that a particle existed which was basic to all matter. It has only been
in the last century and a half that we have learned that even the atom itself is
made up of even more basic particles - the electron, proton, and neutron (J.J. Thompson
found the electron in 1897, which was postulated by G. Johnstone Stoney in 1947).
It wasn't until the 1930s that even those three entities were thought to be constructed
of yet more fundamental particles - quarks, bosons, and leptons. Modern science
believes it has fully defined the set of subatomic particles, particularly with
the Higgs boson having been finally seen in the Large Hadron Collider (well, maybe).
Does anyone really believe this is the final word on fundamental particles after
having been proved wrong so many times?The World Within the Atom
... an atomic detective story

Atomic cloud chamber "footprints" have shed new light on the
inner world of the atom.
By Saunder Harris, WINXL
Believe it or not, our Atomic Age is over 2500 years old. It all started back
with the ancient Greek philosophers. One in particular, named Democritus, suggested
that a particle existed which was basic to all matter. This particle, he said, was
invisible and could not be divided. The Greeks had a name for it ... they called
it the atom.
Early Atomics
This idea of a basic particle or substance was more hunch than scientific theory,
and it took thousands of years before it could be put to test. Our present concept
of the atom began with the work of John Dalton, an English chemist, who first described
the laws of chemical compounds and elements in 1802. He separated matter down to
its basic building blocks, the elements.
To visualize Dalton's discoveries, imagine that we have a basket of mixed
citrus fruit. The complete basket with all the various fruits would be comparable
to a chemical compound. If we took out the fruits and separated them into groups
of lemons, oranges, grapefruit and so on, we would be breaking the compound down
into its elements. Then, if we set apart one orange, for example, we would be isolating
a single atom. The next step would be to peel the orange and take a bite of the
fruit within. In the case of the atom, this first bite was taken by the English
physicist, Sir Joseph J. Thomson, in 1897.
 Fig. 1 - Thomson was
able to calculate the ratio of the electron's charge to its mass by bending
the electron beam with known electrostatic and magnetic fields.

Fig. 2 - Cloud chambers such as the one above at the Brookhaven National
Laboratory provide clues for atomic detectives. The device bombards atomic nuclei
with billion-volt nuclear particles. Atomic fragments leave a path in the moist,
gas-filled air which can be photographed and interpreted.

Diagram shows basic construction of cloud chamber.

Tracks left by high-speed protons on a sheet of photographic film are
shown at left. The dotted horizontal lines were made by protons. The "star"
was made when an atom disintegrated in the photographic emulsion. (Brookhaven Lab
photo)


Cosmotron at the Brookhaven National Laboratory accelerates particles
to energies of two or three billion volts. Inside diameter of the Cosmotron is over
60 feet.
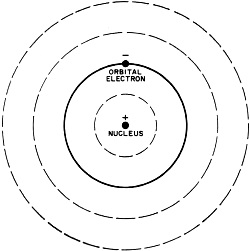
Fig. 3 - Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom. Solid line indicates
normal orbit of the planetary electron. When electron moves to inner orbit, energy
in the form of light is given off. When energy in the form of heat is applied, the
electron wll move to the outer orbits.
Discovering the Electron
During the middle years of the 19th
century, scientists had discovered that if an electric current were passed between
two electrodes placed at the ends of a partially evacuated glass tube, a visible
beam of unknown nature would travel from negative to positive electrode. Experiments
indicated that this beam was negative in its electrical charge.
Sir J. J. Thomson, using the apparatus shown in Fig. 1, was able to compute
the ratio of the charge of a single particle in the beam to its mass. In so doing
he proved that the beam was composed of individual, negatively charged particles.
This was the discovery of the electron.
In other experiments, Thomson tried using various gases in the tube, but in each
case his results were the same. The particle was independent of the material from
which it came. Thomson therefore concluded that the electron was a basic constituent
of all atoms.
You can see that Thomson's apparatus was similar to our cathode-ray tube.
In fact, the picture tube in your TV set is a direct descendant of the one Thomson
used. If you take a strong magnet and place it against the face of the tube while
the set is on, you will see a distortion caused by the magnetic field bending the
tube's negative electron beam. This is essentially the same effect that led
Thomson to identify the electron.
The Proton
The discovery of the electron was only the first step in the exploration of the
inner world of the atom. Since the atom was known to be electrically neutral, the
physicist now began to search for the positive particles which would balance out
the negative charge of the electron.
In 1914, another English physicist, Sir Ernest Rutherford, found such a positive
particle and called it the proton. The electron's charge was assigned a value
of -1 and the proton's charge a value of +1. Besides the difference in charge,
it was also discovered that the proton was much greater in mass than the electron.
It was, in fact, 1836 times the mass of its smaller opposite.
Obviously, a proton is too small to be seen directly, and you may wonder how
it was detected. Consider a trail left in the sky by a jet plane traveling at high
speed. By looking at such a trail you can follow the flight of the jet without actually
seeing the plane. On a smaller scale, this is how atomic particles are observed.
Figure 2 shows a cloud chamber, a major tool in the detection of atomic particles.
As high-speed particles pass through the cloud chamber, they produce ions in
the chamber's gas-filled atmosphere. When the piston in the bottom of the cloud
chamber is suddenly lowered, this gas, which is saturated with water vapor, expands
and drops in temperature. Water vapor condenses on the ions and outlines the path
of atomic particles through the gas. Photographs can be made of the ion tracks,
and by studying photos of the trails, physicists are able to identify the mass and
charge of the various particles.
Bohr's Atomic Model
In physics, when a theory is proposed, the known facts are often organized by
fitting them into a model. Based on this model, observations are explained and predictions
are made. Our present understanding of the atom has come about in such a manner.
The first proposed model of the atom suggested that it was spherical, like a
golf ball, and that its mass consisted of protons with rings of electrons between
them. This model, however, did not explain certain phenomena such as atoms giving
off light when excited electrically or by heat. It remained for a Danish physicist,
Niels Bohr, to offer a model which would explain these phenomena.
Bohr's conception of the simplest atom, the hydrogen atom, consisted of a
positively charged nucleus with a "planetary" electron in orbit around
it. To move around the nucleus, the electron had to be influenced by some force.
This force, Bohr said, was the electrostatic attraction of the positive proton nucleus
for the outer electron. Figure 3 shows a model of the Bohr atom. Bohr was able to
explain with mathematics many of the experimental results which were obtained through
the use of his model.
Isotopes
In 1932 a new particle was unexpectedly discovered. While experimenting with
radioactive polonium, German scientists detected a strong, penetrating radiation.
In France, the Curies noticed that the placing of a substance containing hydrogen
in the path of this radiation caused the release of high energy protons. These results
were analyzed in the laboratory of James Chadwick, an English physicist, and it
was determined that the radiation was a new type of particle which had no charge.
This third particle was called the neutron.
The fact that various atoms of the same element had been found to have different
weights could now be explained by the difference in the number of neutrons in their
nuclei. For example, there are three types of hydrogen. H1 has a nucleus
which contains one proton. H2 has a proton and a neutron in the nucleus.
The heaviest, H3, so rare that only three pounds of it are thought to
exist on earth, has one proton and two neutrons in the nucleus. Atoms with an "excess"
of neutrons are called isotopes.
Isotopes can appear in all elements. The important thing to remember is that
planetary electrons in the outer orbits balance the number of protons in the nucleus.
Energy and Radioactivity
With our three particles, the electron, the proton, and the neutron, we could
set up a mechanical model of the atom such as Bohr's. This model would account
for most of the things physicists have observed. What it would not do is explain
how mass could be converted into energy (and energy into mass) without loss. In
other words, the fly in the atomic ointment would be Einstein's famous equation
E = MC2 (energy = mass times speed of light squared).
According to Einstein, it is possible to change these two, mass and energy, into
each other without a loss. The three-particle model of the atom could not mathematically
explain how this is possible. Physicists were thus forced to the realization that
there was more to the atom than the electron, the proton, and the neutron.
The first inkling that there was energy in the atom came about through the studies
of Curie and Becquerel in the field of radio-activity. Three different types of
radiation were found to be given off by naturally radioactive radium and uranium:
alpha, beta and gamma rays. The alpha and beta rays were high-speed particles while
the gamma rays were found to be powerful streams of energy with 100 times the penetrating
power of beta particles.
Investigating these radiations in the light of Einstein's equation, physicists
found that the energy given off did not balance with the loss of mass. In order
for everything to balance, the Italian physicist, Enrico Fermi, suggested still
another particle. This he called the neutrino or "little neutral one."
Fermi theorized that the neutrino would have to be almost pure energy to make the
scales balance. It would also be very difficult to detect because of its high speed
and lack of charge and mass. It was finally found in 1956 through delicate atomic
detective work, a major scientific triumph.
Atom Smashers
When the big "atom smashers" were built. scientists were given the
necessary tools for probing the inner atom. There are many types of atom smashers,
or particle accelerators, their scientific name. Among them are the cyclotron, the
betatron, and the cosmotron.
Without going into detail on their operation, it is enough to understand that
the atom smashers whirl ions of gas around in circular paths by electrical and magnetic
means. These ions increase in velocity until they approach the speed of light. They
are then deflected magnetically into an opening where they bombard the nuclei of
substances under study. If you have ever whirled a stone on a string and had the
string break, you will understand the principle of an atom smasher.
With the aid of these giant scientific instruments, some of them filling huge
buildings, more new particles were discovered. Many of these had been mathematically
predicted - and now they were revealed. A particle was found which was the same
as the electron, but opposite in charge: it was called a positron or positive electron.
Then in the 1950's an important announcement ... the discovery of anti-matter.
 Anti-Matter Anti-Matter
The French physicist, Dirac, mathematically concluded that each of the basic
particles should have an opposite, or anti-particle. Four such anti-particles were
found.
Anti-matter proved very difficult to detect because of its short life; the anti-matter
particles combine with their opposites and annihilate each other almost instantly.
Gamma rays equal to their former mass are given off. It is thought that anti-matter
differs from its opposite only in that its magnetic poles are reversed, with each
particle being considered a small magnet.
Mesons and Hyperons
Next, two other particles were found: the meson, whose existence was predicted
by the Japanese physicist, Yukawa, and the hyperon, the most massive of all atomic
particles. These are each actually families of particles, rather than single units.
Mesons and hyperons are believed to" act as a "glue" which binds
the particles of the nucleus together.
Where do we go from here? Our 2500- year search for an understanding of matter
is far from being finished. There is still no final model of the atom. Man has yet
to find the. complete answer to nature's atomic puzzle.
Posted October 5, 2022
|












 Anti-Matter
Anti-Matter


