|
In calculus, a branch of
mathematics, the derivative is a measure of how a function changes as its input changes. Loosely speaking, a
derivative can be thought of as how much a quantity is changing at a given point. For example, the derivative of
the position (or distance) of a vehicle with respect to time is the instantaneous velocity (respectively,
instantaneous speed) at which the vehicle is travelling. Conversely, the integral of the velocity over time is the
vehicle's position. The derivative of a function at a chosen input value describes the best linear
approximation of the function near that input value. For a real-valued function of a single real variable, the
derivative at a point equals the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at that point. In higher
dimensions, the derivative of a function at a point is a linear transformation called the linearization. A closely
related notion is the differential of a function. The process of finding a derivative is called
differentiation. The fundamental theorem of calculus states that differentiation is the reverse process to
integration.
- Wikipedia
| If f (x) and g (x) are differentiable, then
[ f (x) g (x) ] ' = f (x) g ' (x) + g (x) f ' (x)
|
If f (x) and g (x) are differentiable and g (x) ¹ 0, then
 |
If f (x) = xn, where n is a positive integer, then f ' (x) = n xn-1
|
If y = f (u) and u = g (x) and both are differentiable, then 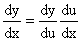
|
|








