 In electronics and electrical engineering, fuses are used to prevent an overcurrent
condition from damaging the circuit that it is designed to protect. Fuses come in
many shapes, sizes, current limits, and operational voltages. The primary component
in the fuse it usually a metal wire whose length, diameter, and alloy composition
is tailored to melt (fuse) at a precise current value. In electronics and electrical engineering, fuses are used to prevent an overcurrent
condition from damaging the circuit that it is designed to protect. Fuses come in
many shapes, sizes, current limits, and operational voltages. The primary component
in the fuse it usually a metal wire whose length, diameter, and alloy composition
is tailored to melt (fuse) at a precise current value.
Two basic types of fuses are available - fast reaction and slow reaction. Fast
reaction fuses are used to protect circuit that cannot tolerate even a small amount
of excessive current. The sensitive gate of a semiconductor device is an example.
Slow reaction (slow-blow) fuses are used for circuits where a higher than normal
current condition can be survived for a short time, such as a motor when it first
starts (inrush current can be many times greater than the normal run current).
Fuse drawing page
Fuse
vendor page
In addition to the sizes represented here, surface mount (SMT) packages are available
in standard outlines beginning as small as 0603 (0.063" x 0.031"). See
Fuse
vendor listing.
| 1AG (AGA) glass
|
1/4 |
5/8 |
125 32
|
1/16,1/10,1/8,1/4 3/8,1/2,6/10,3/4,1
1-1/2,2,2-1/2,3,5
6,7,7-1/2,10,15,
20,25,30
|
| 2AG (225) glass
|
0.177 |
0.588 |
250 125
|
1/10,1/8,1/4,3/8 1/2,3/4,1,1-1/2,2
2-1/2,3,3-1/2 4,5,6,7,8,10
|
| 3AG (AGC) glass
|
1/4 |
1-1/4 |
250 32
|
1/20,1/16,1/10,1/8,3/16 2/10,1/4,3/10,3/8,1/2,3/4
1,1-1/4,1-1/2,2,2-1/4
2-1/2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 15,20,25,30
|
| 3AB (ABC) ceramic
|
1/4 |
1-1/4 |
250 125
|
1/8,1/4,1/2,3/4,1,2 3,4,5,6,7,8,10,12
15,20 25,30
|
| 4AG (AG) |
9/32 |
1-1/4 |
|
|
| 5AG (AGU) glass
|
13/32 |
1-1/2 |
250
32
|
1,2,3 4,5,8,10,15,20,25 30,35,40,50,60
|
| 7AG (AGW) glass
|
1/4 |
7/8 |
32 |
1,1-1/2,2,2-1/2,3 4,5,6,7-1/2,10,15
20,25,30
|
| 8AG (AGX) glass
|
1/4 |
1 |
250
125
32
|
1/500,1/200,1/100
1/32,1/16,1/10,1/8
2/10,3/16,1/4,3/10
3/8,4/10,1/2,3/4,1
1-1/4,1-1/2,22-1/2,3,4,5,6,7 8,10,15,20,25,30
|
| 5x15mm (C519,C520)
glass
|
5 mm |
15 mm |
250
125
|
125mA,250mA,350mA 375mA,500mA,600mA
750mA,1,1.25,1.5,1.62,2.5,3,3.5,4,5
|
| 5x20mm (GDA,GDB)
glass
|
5 mm |
20 mm |
250 |
50mA,63mA,80mA,100mA 125mA,160mA,200mA
250mA,315mA,400mA,500mA
630mA,800mA,1,1.25,1.6
2,2.5,3.15,4,5,6.3,8,10
|
| Nanofuse |
0.080 |
0.225 |
125 60
32
|
1/16,1/8,1/4 3/8,1/2 3/4,1,1-1/2,2
2-1/2,3,3-1/2,4 5,7,10,12,15
|
| SFE |
1/4 |
5/8 to 1-7/16 |
|
|
| Automotive (ATC)
blade
|
0.207 (W) 0.752 (H)
|
0.760 |
32 |
Black = 1A Gray = 2A
Violet = 3A
Pink = 4A
Tan = 5A
Brown = 7½
Red = 10A
Blue = 15A
Yellow = 20A
Clear = 25A
Green = 30A
Amber = 40A
|
| Mini Auto (ATM)
blade
|
0.15 (W) 0.429 (H)
|
0.760 |
32 |
Gray = 2A Violet = 3A
Pink = 4A
Tan = 5A
Brown = 7½
Red = 10A
Blue = 15A
Yellow = 20A
Clear = 25A
Green = 30A
|
| Note: The "AG" term
comes from Automobile Glass fuse. |
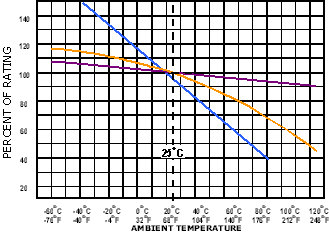
| Specify fuse current as: Nominal Operating
Current / 0.75, at 25ºC, then derate fuse current above or below 25°C per chart.
|
| Derating: |
A = Slow Blow B = Fast
C = Resettable
|
|
|








