 All RF Cafe Quizzes make great fodder for
employment interviews for technicians or engineers - particularly those who are
fresh out of school or are relatively new to the work world. Come to think of it,
they would make equally excellent study material for the same persons who are going
to be interviewed for a job. Bonne chance, Viel Glück, がんばろう,
buena suerte, удачи, in bocca al lupo, 행운을 빕니다,
ádh mór, בהצלחה, lykke til, 祝你好運.
Well, you know what I mean: Good luck! All RF Cafe Quizzes make great fodder for
employment interviews for technicians or engineers - particularly those who are
fresh out of school or are relatively new to the work world. Come to think of it,
they would make equally excellent study material for the same persons who are going
to be interviewed for a job. Bonne chance, Viel Glück, がんばろう,
buena suerte, удачи, in bocca al lupo, 행운을 빕니다,
ádh mór, בהצלחה, lykke til, 祝你好運.
Well, you know what I mean: Good luck!
Click here for the complete list of
RF Cafe Quizzes.
Note: Some material based on books have quoted passages.
This Analog & RF Filter Basics Quiz targets
those of you who are relative newcomers to the world of radio frequency (RF) electronics,
but seasoned vets are welcome to give it a go as well. It addresses frequency response
and physical construction. Images were obtained from
Anatech Electronics
documents titled "Guideline for Choosing RF and Microwave Products" and "Understanding Filter Types and Their Characteristics." API Technologies'
"RF &
Microwave Filters," is also referenced. Please report any suspected errors to
me via e-mail. Return to Quiz #70.
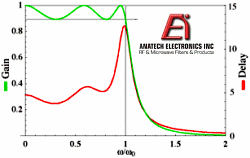 1.
The plot to the right is representative of amplitude and group delay responses for
which type of analog filter? 1.
The plot to the right is representative of amplitude and group delay responses for
which type of analog filter?
c) Chebyshev
Cheyshev filters exhibit amplitude ripple in the passband and monotonic roll-off
in the stopband.
  2. The photo to the right
represents which type of filter construction? 2. The photo to the right
represents which type of filter construction?
a) Cavity b) Ceramic c) Crystal d) Lumped element L/C
(inductor/capacitor) e) Tubular
a) Cavity
Cavity filters use a coil inside a cavity for interstage coupling and resonance.
They typically have a very high "Q" and low insertion loss.
 3.
The plot to the right is representative of amplitude and group delay responses for
which type of analog filter? 3.
The plot to the right is representative of amplitude and group delay responses for
which type of analog filter?
a) Bessel b) Butterworth c) Chebyshev d) Elliptical e) Ideal
e) Ideal
An ideal filter exhibits perfectly flat amplitude and group delay (and phase)
in the passband and infinite attenuation in the stopband. As the name implies, ideal
filters cannot be realized in the real world.
 4. The
photo to the right represents which type of filter construction? 4. The
photo to the right represents which type of filter construction?
a) Cavity b) Ceramic c) Crystal d) Lumped element L/C
(inductor/capacitor) e) Tubular
b) Ceramic
Ceramic filters exploit the electromechanical resonance of the substrate to pass
or reject signals depending on the frequency.
 5.
The plot to the right is representative of amplitude and group delay responses for
which type of analog filter? 5.
The plot to the right is representative of amplitude and group delay responses for
which type of analog filter?
a) Bessel b) Butterworth c) Chebyshev d) Elliptical e) Ideal
a) Bessel
Bessel filters are referred to as maximally flat group delay filters with no
deviation at the band edge, as the plot demonstrates.
 6. The
photo to the right represents which type of filter construction? 6. The
photo to the right represents which type of filter construction?
a) Cavity b) Ceramic c) Crystal d) Lumped element L/C
(inductor/capacitor) e) Tubular
d) Lumped element L/C (inductor/capacitor)
A lumped element filter uses actual physical inductors and capacitors as resonant
elements to determine whether specific frequencies are passed or blocked.
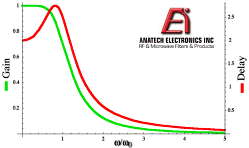 7. The plot to the right is representative
of amplitude and group delay responses for which type of analog filter? 7. The plot to the right is representative
of amplitude and group delay responses for which type of analog filter?
a) Bessel b) Butterworth c) Chebyshev d) Elliptical e) Ideal
b) Butterworth
Butterworth filters are referred to as maximally flat amplitude filters because
the passband does not have any insertion loss ripple.
  8. The photo to the right
represents which type of filter construction? 8. The photo to the right
represents which type of filter construction?
a) Cavity b) Ceramic c) Crystal d) Lumped element L/C
(inductor/capacitor) e) Tubular
e) Tubular
Tubular (aka Coaxial) filters have inherently broad stopbands with very high
rejection levels. They are often inserted inline with coaxial cable interconnects
when unplanned interference needs to be handled.
 9.
The plot to the right is representative of amplitude and group delay responses for
which type of analog filter? 9.
The plot to the right is representative of amplitude and group delay responses for
which type of analog filter?
a) Bessel b) Butterworth c) Chebyshev d) Elliptical e) Ideal
d) Elliptical
Elliptical (aka Cauer) filters have the highest theoretical stopband attenuation
roll-off for a given number of poles.
 10. The
photo to the right represents which type of filter construction? 10. The
photo to the right represents which type of filter construction?
a) Cavity b) Ceramic c) Crystal d) Lumped element L/C
(inductor/capacitor) e) Tubular
c) Crystal
Crystal filters rely on the electromechanical resonance properties of (most often)
quartz crystals that are shaped and sized for resonance at specific frequencies.
Posted August 19, 2020
|



 1.
The plot to the right is representative of amplitude and group delay responses for
which type of analog filter?
1.
The plot to the right is representative of amplitude and group delay responses for
which type of analog filter? 

 3.
The plot to the right is representative of amplitude and group delay responses for
which type of analog filter?
3.
The plot to the right is representative of amplitude and group delay responses for
which type of analog filter?  4. The
photo to the right represents which type of filter construction?
4. The
photo to the right represents which type of filter construction?  5.
The plot to the right is representative of amplitude and group delay responses for
which type of analog filter?
5.
The plot to the right is representative of amplitude and group delay responses for
which type of analog filter?  6. The
photo to the right represents which type of filter construction?
6. The
photo to the right represents which type of filter construction?  7. The plot to the right is representative
of amplitude and group delay responses for which type of analog filter?
7. The plot to the right is representative
of amplitude and group delay responses for which type of analog filter? 

 9.
The plot to the right is representative of amplitude and group delay responses for
which type of analog filter?
9.
The plot to the right is representative of amplitude and group delay responses for
which type of analog filter?  10. The
photo to the right represents which type of filter construction?
10. The
photo to the right represents which type of filter construction? 


