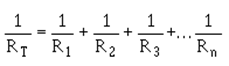Module 1 - Introduction to Matter, Energy, and Direct Current |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Module 1 − Introduction to Matter, Energy, and Direct Current
Pages i, 1−1, 1−11, 1−21, 1−31, 1−41, 1−51, 1−61, 2−1, 2−11, 2−21, 3−1, 3−11, 3−21, 3−31, 3−41, 3−51, 3−61, 3−71, 3−81, 3−91, 3−101, 3−111, 3−121, Appendix I, II, III, IV, V, Index
Appendix I Glossary AMMETER - An instrument for measuring the amount of electron flow in amperes. Ampere - The basic unit of electrical current. ANODE - a positive electrode of an electrochemical device (such as a primary or secondary electric cell) toward which the negative ions are drawn. ATTRACTION - The force that tends to make two objects approach each other. Attraction exists between two unlike magnetic poles (North and South) or between two unlike static charges (plus and minus). BATTERY - a device for converting chemical energy into electrical energy. BATTERY CAPACITY - The amount of energy available from a battery. Battery capacity is expressed in ampere-hours. BLEEDER CURRENT - The current through a bleeder resistor. In a voltage divider, bleeder current is usually determined by the 10 percent rule of thumb. BLEEDER Resistor - a resistor which is used to draw a fixed current. BRANCH - An individual current path in a parallel circuit. CATHODE - The general name for any negative electrode. CELL - a single unit that transforms chemical energy into electrical energy. Batteries are made up of cells. CHARGE - Represents electrical energy. a material having an excess of electrons is said to have a negative charge. a material having a deficiency of electrons is said to have a positive charge. Circuit - The complete path of an electric current. CIRCULAR MIL - An area equal to that of a circle with a diameter of 0.001 inch. It is used for measuring the cross-sectional area of wires. Combination Circuit - a series-parallel circuit. CONDUCTANCE - The ability of a material to conduct or carry an electric current. It is the reciprocal of the resistance of the material, and is expressed in mhos or siemens. CONDUCTIVITY - Ease with which a substance transmits electricity. CONDUCTOR - (1) a material with a large number of free electrons. (2) a material which easily permits electric current to flow. COULOMB - a measure of the quantity of electricity. One coulomb is equal to 6.28 x 1018 electrons.
AI-1 COULOMB'S LAW - Also called the law of electric charges or the law of electrostatic attraction. Coulomb's Law states that charged bodies attract or repel each other with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their individual charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. CPR - Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation. CROSS-SECTIONAL AREA - The area of a "slice" of an object. When applied to electrical conductors, it is usually expressed in circular mils. CURRENT - The flow of electrons past a reference point. The passage of electrons through a conductor. Measured in amperes. DEAD Short - a short circuit having minimum resistance. Dielectric FIELD - The space between and around charged bodies in which their influence is felt. Also called Electric Field of Force or an Electrostatic Field. Direct CURRENT - An electric current that flows in one direction only. DOMAIN THEORY - a theory of magnetism based upon the electron-spin principle. Spinning electrons have a magnetic field. If more electrons spin in one direction than another, the atom is magnetized. DRY CELL - An electrical cell in which the electrolyte is not a liquid. In most dry cells the electrolyte is in the form of a paste. Efficiency - The ratio of output power to input power, generally expressed as a percentage. ELECTRIC CURRENT - The flow of electrons. ELECTRICAL CHARGE - Symbol Q, q. Electric energy stored on or in an object. The negative charge is caused by an excess of electrons; the positive charge is caused by a deficiency of electrons. ELECTROCHEMICAL - The action of converting chemical energy into electrical energy. ELECTRODE - The terminal at which electricity passes from one medium into another, such as in an electrical cell where the current leaves or returns to the electrolyte. ELECTROLYTE - a solution of a substance which is capable of conducting electricity. An electrolyte may be in the form of either a liquid or a paste. ELECTROMAGNET - An electrically excited magnet capable of exerting mechanical force, or of performing mechanical work. ELECTROMagnetic - The term describing the relationship between electricity and magnetism. Having both magnetic and electric properties. ELECTROMagnetic INDUCTION - The production of a voltage in a coil due to a change in the number of magnetic lines of force (flux linkages) passing through the coil. ELECTRON - The elementary negative charge that revolves around the nucleus of an atom. ELECTRON SHELL - a group of electrons which have a common energy level that forms part of the outer structure (shell) of an atom.
AI-2 ELECTROSTATIC - Pertaining to electricity at rest, such as charges on an object (static electricity). ELEMENT - a substance, in chemistry, that cannot be divided into simpler substances by any means ordinarily available. EMF - (Electromotive Force) The force which causes electricity to flow between two points with different electrical charges or when there is a difference of potential between the two points. The unit of measurement in volts. ENERGY - The ability or capacity to do work. EQUIVALENT Resistance - (Req) a resistance that represents the total ohmic values of a circuit component or group of circuit components. Usually drawn as a single resistor when simplifying complex circuits. FERROMagnetic MATERIAL - a highly magnetic material, such as iron, cobalt, nickel, or alloys, make up these materials. FIELD of forCE - a term used to describe the total force exerted by an action-at-a-distance phenomenon such as gravity upon matter, electric charges acting upon electric charges, magnetic forces acting upon other magnets or magnetic materials. FIXED Resistor - a resistor having a definite resistance value that cannot be adjusted. Flux - In electrical or electromagnetic devices, a general term used to designate collectively all the electric or magnetic lines of force in a region. Flux DENSITY - The number of magnetic lines of force passing through a given area. GAS - One of the three states of matter having no fixed form or volume. (Steam is a gas.) GRAPH - a pictorial presentation of the relation between two or more variable quantities, such as between an applied voltage and the current it produces in a circuit. Ground POTENTIAL - Zero potential with respect to the ground or earth. HORSEPower - The English unit of power, equal to work done at the rate of 550 foot-pounds per second. Equal to 746 watts of electrical power. HORSESHOE MAGNET - a permanent magnet or electromagnet bent into the shape of a horseshoe or having a U-shape to bring the two poles near each other. HYDROMETER - An instrument used to measure specific gravity. In batteries hydrometers are used to indicate the state of charge by the specific gravity of the electrolyte. INDUCED CHARGE - An electrostatic charge produced on an object by the electric field that surrounds a nearby object. INDUCED CURRENT - Current due to the relative motion between a conductor and a magnetic field. INDUCED ELECTROMOTIVE forCE - The electromotive force induced in a conductor due to the relative motion between a conductor and a magnetic field. INDUCED Voltage - See Induced Electromotive Force.
AI-3 INDUCTION - The act or process of producing voltage by the relative motion of a magnetic field across a conductor. INFINITE - (1) Extending indefinitely, endless. (2) Boundless having no limits. (3) An incalculable number. INSULATION - (1) a material used to prevent the leakage of electricity from a conductor and to provide mechanical spacing or support to protect against accidental contact. (2) use of material in which current flow is negligible to surround or separate a conductor to prevent loss of current. INSULATOR - (1) Material of such low conductivity that the flow of current through it can usually be neglected. (2) Device having high-electric resistance, used for supporting or separating conductors so as to prevent undesired flow of current from the conductors to other objects. INVERSELY - Inverted or reversed in position or relationship. ION - An electrically charged atom or group of atoms. Negative ions have an excess of electrons; positive ions have a deficiency of electrons. IONIZE - To make an atom or molecule of an element lose an electron, as by X-ray bombardment, and thus be converted into a positive ion. The freed electron may attach itself to a neutral atom or molecule to form a negative ion. JUNCTION - (1) The connection between two or more conductors. (2) The contact between two dissimilar metals or materials, as is in a thermocouple. KILO - a prefix meaning one thousand. KINETIC ENERGY - Energy which a body possesses by virtue of its motion. KIRCHHofF'S LAWS - (1) The algebraic sum of the currents flowing toward any point and the current flowing from that point in an electric network is zero. (2) The algebraic sum of the products of the current and resistance in each of the conductors in any closed path in a network is equal to the algebraic sum of the electromotive forces in the path. LAW of MAGNETIsM - Like poles repel; unlike poles attract. LEAD-ACID CELL - a cell in an ordinary storage battery, in which electrodes are grids of lead containing an active material consisting of certain lead oxides that change in composition during charging and discharging. The electrodes or plates are immersed in an electrolyte of diluted sulfuric acid. LINE of forCE - a line in an electric or magnetic field that shows the direction of the force. LIQUID - One of the three states of matter which has a definite volume but no definite form. (Water is a liquid.) Load - (1) a device through which an electric current flows and which changes electrical energy into another form. (2) Power consumed by a device or circuit in performing its function. LOCAL ACTION - a continuation of current flow within an electrical cell when there is no external load. Caused by impurities in the electrode. Magnetic FIELD - The space in which a magnetic force exists.
AI-4 Magnetic POLES - The section of a magnet where the flux lines are concentrated; also where they enter and leave the magnet. MAGNETIsM - The property possessed by certain materials by which these materials can exert mechanical force on neighboring masses of magnetic materials; and can cause currents to be induced in conducting bodies moving relative to the magnetized bodies. MATTER - Any physical entity which possesses mass. MEGA - a prefix meaning one million, also Meg. MHO - Unit of conductance: the reciprocal of the ohm. Replaced by siemens. MICRO - a prefix meaning one-millionth. MILLI - a prefix meaning one-thousandth. Negative ELECTRODE - a terminal or electrode having more electrons than normal. Electrons flow out of the negative terminal of a voltage source. Negative TEMPERATURE COEFFICIENT - The temperature coefficient expressing the amount of reduction in the value of a quantity, such as resistance for each degree of increase in temperature. Network - a combination of electrical components. In a parallel circuit it is composed of two or more branches. NEUTRAL - In a normal condition, hence neither positive nor negative. a neutral object has a normal number of electrons. OHM - The unit of electrical resistance. It is that value of electrical resistance through which a constant potential difference of 1 volt across the resistance will maintain a current flow of 1 ampere through the resistance. OHMIC Value - Resistance in ohms. OHM'S LAW - The current in an electric circuit is directly proportional to the electromotive force in the circuit. The most common form of the law is E = IR, where E is the electromotive force or voltage across the circuit, I is the current flowing in the circuit, and R is the resistance of the circuit. OPEN Circuit - (1) The condition of an electrical circuit caused by the breaking of continuity of one or more conductors of the circuit; usually an undesired condition. (2) a circuit which does not provide a complete path for the flow of current. PARALLEL Circuit - Two or more electrical devices connected to the same pair of terminals so separate currents flow through each; electrons have more than one path to travel from the negative to the positive terminal. PERMEABILITY - The measure of the ability of a material to act as a path for magnetic lines of force. PHOTOELECTRIC Voltage - a voltage produced by light. PICO - a prefix adopted by the National Bureau of Standards meaning 10-12.
AI-5 PIEZOELECTRIC EFFECT - The effect of producing a voltage by placing a stress, either by compression, expansion, or twisting, on a crystal and, conversely, producing a stress in a crystal by applying a voltage to it. PLATE - One of the electrodes in a storage battery. POLARITY - (1) The condition in an electrical circuit by which the direction of the flow of current can be determined. Usually applied to batteries and other direct voltage sources. (2) Two opposite charges, one positive and one negative. (3) a quality of having two opposite magnetic poles, one north and the other south. POLARIZATION - The effect of hydrogen surrounding the anode of a cell which increases the internal resistance of the cell. POTENTIAL ENERGY - Energy due to the position of one body with respect to another body or to the relative parts of the same body. POTENTIOMETER - a 3-terminal resistor with one or more sliding contacts, which functions as an adjustable voltage divider. Power - The rate of doing work or the rate of expending energy. The unit of electrical power is the watt. PRIMARY CELL - An electrochemical cell in which the chemical action eats away one of the electrodes, usually the negative electrode. RECIPROCAL - The value obtained by dividing the number 1 by any quantity. REFERENCE Point - a point in a circuit to which all other points in the circuit are compared. RELUCTANCE - a measure of the opposition that a material offers to magnetic lines of force. REPULSION - The mechanical force tending to separate bodies having like electrical charges or like magnetic polarity. RESIDUAL MAGNETIsM - Magnetism remaining in a substance after removal of the magnetizing force. Resistance - (1) The property of a conductor which determines the amount of current that will flow as the result of the application of a given electromotive force. All conductors possess some resistance, but when a device is made especially for the purpose of limiting current flow, it is called a resistor. a resistance of 1 ohm will allow a current of 1 ampere to flow through it when a potential of 1 volt is applied. (2) The opposition which a device or material offers to the flow of current. The effect of resistance is to raise the temperature of the material or device carrying the current. (3) a circuit element designed to offer a predetermined resistance to current flow. Resistor - The electrical component which offers resistance to the flow of current. It may be a coil of fine wire or a composition rod. RETENTIVITY - The ability of a material to retain its magnetism. RHEOSTAT - (1) a resistor whose value can be varied. (2) a variable resistor which is used for the purpose of adjusting the current in a circuit.
AI-6 SCHEMATIC Circuit Diagram - a circuit diagram in which component parts are represented by simple, easily drawn symbols. May be called schematic. SCHEMATIC SYMBOLS - a letter, abbreviation, or design used to represent specific characteristics or components on a schematic diagram. SECONDARY CELL - a cell that can be recharged by passing a current through the cell in a direction opposite to the discharge current. Series Circuit - An arrangement where electrical devices are connected so that the total current must flow through all the devices; electrons have one path to travel from the negative terminal to the positive terminal. Series-PARALLEL Circuit - a circuit that consists of both series and parallel networks. SHELF LIFE - The period of time that a cell or battery may be stored and still be useful. SHIELDING - a metallic covering used to prevent magnetic or electromagnetic fields from effecting an object. Short Circuit - a low resistance connection between two points of different potential in a circuit, usually accidental and usually resulting in excessive current flow that may cause damage. SIEMANS - The new and preferred term for mho. SOLID - One of the three states of matter which has definite volume and shape. (Ice is a solid.) SOURCE Voltage - The device which furnishes the electrical energy used by a load. SPECIFIC GRAVITY - The ratio between the density of a substance and that of pure water at a given temperature. STATIC ELECTRICITY - Stationary electricity that is in the form of a charge. The accumulated electric charge on an object. Switch - a device to connect, disconnect, or change the connections in an electrical circuit. TAPPED Resistor - a wire-wound, fixed resistor having one or more additional terminals along its length, generally for voltage-divider applications. TEMPERATURE COEFFICIENT - The amount of change of resistance in a material per unit change in temperature. TERMINAL - An electrical connection. THERMOCOUPLE - a junction of two dissimilar metals that produces a voltage when heated. TOLERANCE - (1) The maximum error or variation from the standard permissible in a measuring instrument. (2) a maximum electrical or mechanical variation from specifications which can be tolerated without impairing the operation of a device.
AI-7 TOTAL Resistance - (RT) The equivalent resistance of an entire circuit. For a series circuit: RT = R1 + R2 + R3 . . . Rn. For parallel circuits:
UNIDirectIONAL - In one direction only. VALENCE - The measure of the extent to which an atom is able to combine directly with other atoms. It is believed to depend on the number and arrangement of the electrons in the outermost shell of the atom. VALENCE SHELL - The electrons that form the outermost shell of an atom. VARIABLE Resistor - a wire-wound or composition resistor, the value of which may be changed. VOLT - The unit of electromotive force or electrical pressure. One volt is the pressure required to send 1 ampere of current through a resistance of 1 ohm. Voltage - (1) The term used to signify electrical pressure. Voltage is a force which causes current to flow through an electrical conductor. (2) The voltage of a circuit is the greatest effective difference of potential between any two conductors of the circuit Voltage DIVIDER - a series circuit in which desired portions of the source voltage may be tapped off for use in equipment. Voltage DROP - The difference in voltage between two points. It is the result of the loss of electrical pressure as a current flows through a resistance. WATT - The practical unit of electrical power. It is the amount of power used when one ampere of dc flows through a resistance of one ohm. WATTAGE RATING - a rating expressing the maximum power that a device can safely handle. WATT-HOUR - a practical unit of electrical energy equal to one watt of power for one hour. WEBER'S THEORY - a theory of magnetism which assumes that all magnetic material is composed of many tiny magnets. a piece of magnetic material that is magnetized has all of the tiny magnets aligned so that the north pole of each magnet points in one direction. Wire - a solid or stranded group of solid, cylindrical conductors having low resistance to current flow, with any associated insulation. WORK - The product of force and motion.
AI-8
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||